How to transform an HTML 5 mobile app into an HTML 5 mini program
This topic describes the process to transform an HTML5 mobile app (native app) into an HTML5 mini program. With the web development approach, this transformation makes it possible to have a scalable solution while keeping the digital experience consistent.
The following two types of mini programs are supported on Mini Program Platform:
- Mini Program based on DSL (Domain Specific Language)
We recommend that you develop the default DSL-based mini programs. For more information, see About Mini Program.
- Mini Program based on HTML5
However, to help you integrate your existing HTML5 mobile apps with the wallet app, you can choose the HTML5 mini program type.
What are HTML5 mini programs?
HTML5 mini programs are the mini programs that are transformed from HTML5 mobile apps. HTML5 mini programs run in the WebView environment, so you can develop HTML5 mini programs as you do for web pages. Compared with HTML5 mobile apps, HTML5 mini programs are powered with more capabilities by calling mini program JSAPIs, thus improving user experience.
Benefits
There is no need to start from scratch if you already have an existing HTML5 mobile app. Different roles can enjoy the following benefits by transforming your HTML5 app into a mini program:
- Convenient
As compared with the time-consuming learning of the Mini Program framework, developers can reuse their familiar web development knowledge to get started with Mini Program.
- Cost-efficient
Merchants, ISVs, and wallet developers just need to add a few lines of JavaScript code to the existing HTML5 app, and the HTML5 mini programs become ready.
- Consistent and user-friendly
End users can also benefit from a consistent user experience of mini programs and native apps.
Before you start
Before you start, make sure you have applied for an account and get on-boarded.
Also, you can see the following process flow to get an overview of the detailed steps:
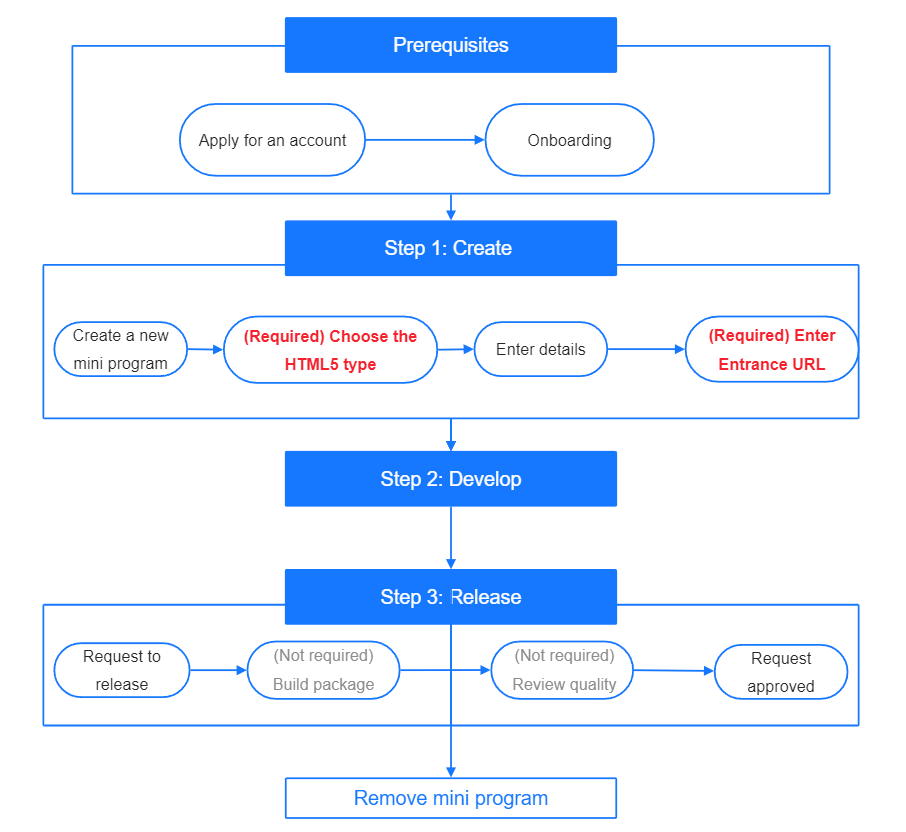
Note:
As compared with the steps of DSL mini programs, the following steps that are shown in red in the above process flow are required:
- HTML5 mini program type
- Entrance URL
Entrance of the HTML5 mini program. You can modify the entrance URL after the HTML5 mini program is created.
The following steps that are shown in gray in the above process flow are optional:
- IDE
You can develop the HTML5 mini programs just like you develop HTML5 web pages.
- Build package process
- Quality review
See procedures for a step-by-step guide on how to transform an HTML5 mobile app (native app) into an HTML5 mini program.
Procedures
To transform HTML5 apps to mini programs, complete the following steps:
Step 1: Create the HTML 5 mini program
When you create a new mini program, choose Mini Program Based on HTML5 and enter the URL of your HTML5 mobile app into the Entrance URL field.

For more information on creating mini programs, see Create Mini Programs.
Step 2: Use wallet capabilities
To use the mini program JSAPIs, integrate the SDK according to your business requirements.
a. Mini Program JSAPIs in HTML5
Follow the steps below to use mini program JSAPIs in HTML5:
- Import the JSBridge SDK by importing the following JS file to the HTML file:
<script src="https://cdn.marmot-cloud.com/npm/hylid-bridge/1.0.5/index.js"></script>See the following HTML sample codes for reference:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Miniprogram JSAPI Demo</title>
<script src="https://cdn.marmot-cloud.com/npm/hylid-bridge/1.0.5/index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button id="alert">my.alert</button>
</div>
<script>
var alertButton = document.getElementById('alert');
alertButton.addEventListener('click', function () {
my.alert({
title: 'Test Alert!!',
content: window.navigator.userAgent,
buttonText: 'Alert Button',
success: function (res) {
my.alert({
content: 'success!' + JSON.stringify(res),
});
},
fail: function () {
my.alert({
content: 'fail!',
});
},
complete: function () {
my.alert({
content: 'complete!',
});
},
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>- Call an API from the following available API list. The parameter in the API is an object. Each API has the following properties:
- success: callback function that indicates the successful API calling.
- fail: callback function that indicates the failed API calling.
- complete: callback function that indicates the completed API calling.
Take the my.alert JSAPI as an example. In this API, success, fail, and complete are the common properties. Specific properties are title, content, and buttonText.
For example, see the following sample codes to know how the IAlertOptions interface can be defined:
interface IAlertOptions {
title?: string;
content?: string;
buttonText?: string;
success?: () => void;
fail?: () => void;
complete?: () => void;
}Available API list
The following table lists all available JSAPIs. You can apply for your own JSAPIs if required.
JSAPI Name | Description |
Displays alert box. | |
Displays confirmation box. | |
Prompts a user input | |
Displays a toast, which disappears within certain seconds. | |
Hides a toast. | |
Displays the loading message. | |
Hides the loading message. | |
Sets the navigation bar text and style. | |
Shows navigation bar loading. | |
Hides navigation bar loading. | |
Network request | |
Gets system information. | |
Gets current network status. | |
Guides users to grant the authorization when the permission is needed. | |
Gets user's authorization code. | |
Saves online images to cellphone album. | |
Takes a photo or chooses a photo from the album on the phone. | |
Previews images. | |
Gets image information. | |
Hides keyboard. | |
Stores the data in the specified key in the local cache, which overlaps with the original data corresponding to the key. | |
Gets cached data. | |
Removes cached data. | |
Clears local data cache. | |
Initiates a payment. | |
Jumps to other mini programs. | |
Returns to the previous Mini Program, only when another Mini Program jumps to the current Mini Program. | |
Gets the clipboard data. | |
Sets the clipboard data. | |
Invokes the vibrate ability of the device. | |
Makes a phone call. | |
Selects in multiple levels. | |
Chooses the phone number of a contact person | |
Gets the current geographical location of the user. |
b. Open APIs
Depending on the wallet capabilities, you can use different open APIs.
Step 3: Release the mini program
You can request to release the mini program after the development. Before you submit the release request for approval, you need to check if all the required information is filled in. Enter the required information under Mini Programs > Info if you find some required information is missing. For more information, see Release Mini Programs and Approvals.
Now you have completed the process of transforming the HTML app into a mini program. You can start to manage the mini program on the platform. For more information, see Manage Mini Program.
Precautions
Browser compatibility
When the page is running in a browser, mini program JSAPIs cannot be called. You need to identify whether the page is running in a mini program or a browser by UserAgent, and then take actions accordingly.
See the following sample codes for reference:
if (/MiniProgram/.test(navigator.userAgent)) {
my.tradePay(params)
} else {
// process payment in other browsers.
}UserAgent
UserAgent which is retrieved via navigator.userAgent has some specific fields like MiniProgram, which can be used to identify whether the web page runs as an HTML mini program.
For a whole UserAgent, see the following sample codes for reference:
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 14_4 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Mobile/18D46 ChannelId(35) Ariver/1.0.11 Griver/2.23.0 AppContainer/1.9.1 MiniProgramRestrictions
Reserved objects
my.JSBridge is reserved for global objects defined in the web app runtime, and you cannot modify them.
console.log
The web app runtime strongly depends on the default console.log object in the web context, which cannot be overridden or modified.
